Explore Australia’s Bar Culture
Your ultimate guide to bars, cafes, and nightlife across Australia’s vibrant cities.
Explore Our Main Offerings
Delve into our curated insights and resources tailored for every bar enthusiast, from newcomers to seasoned patrons.
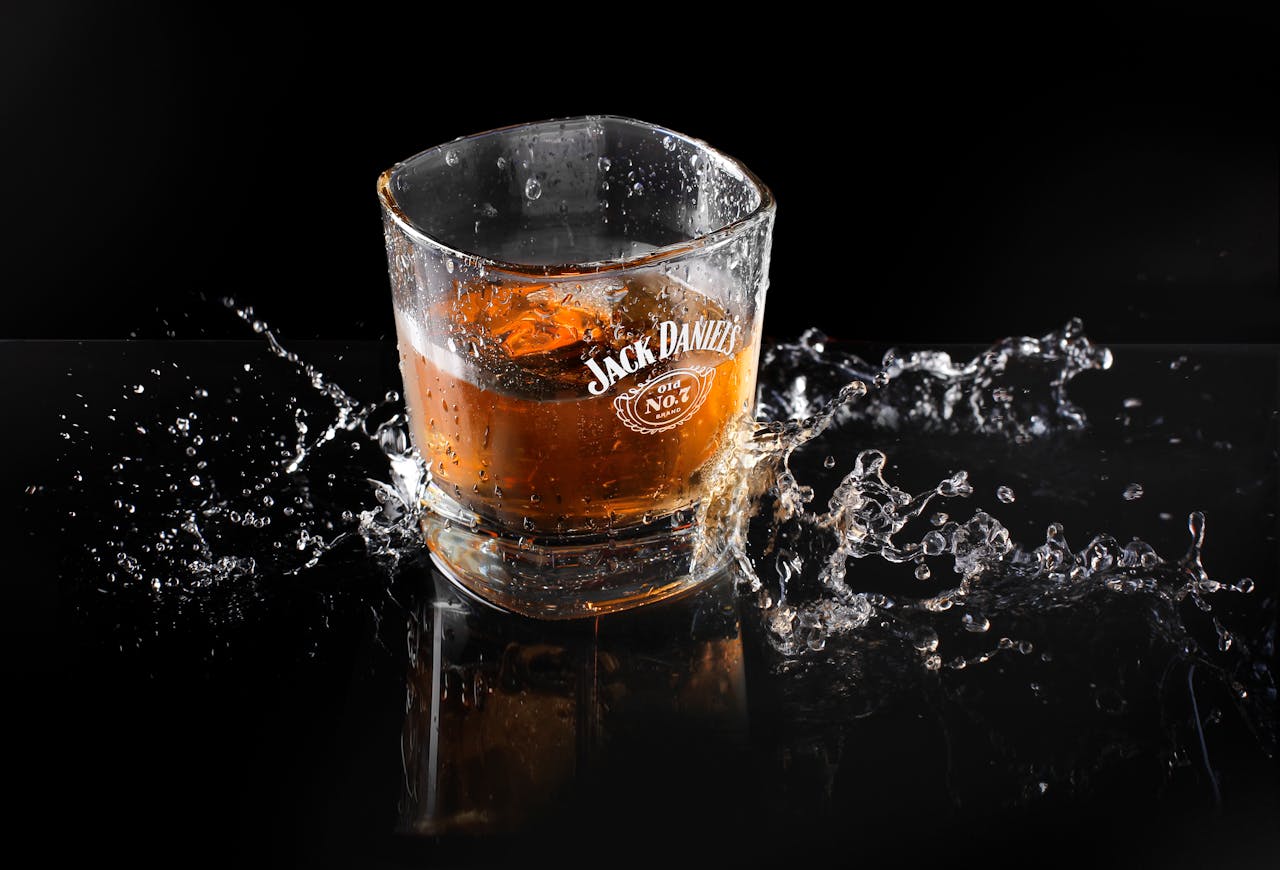

Bar Reviews
Explore in-depth reviews of Australia’s finest bars, cafés, and lounges. Whether you're searching for a cozy corner café in Melbourne, a rooftop cocktail bar in Sydney, or a beachfront hangout in Byron Bay, we’ve got you covered. Our curated insights spotlight both hidden gems and iconic venues, featuring detailed ambiance breakdowns, drink menus, customer service experiences, and local crowd vibes.
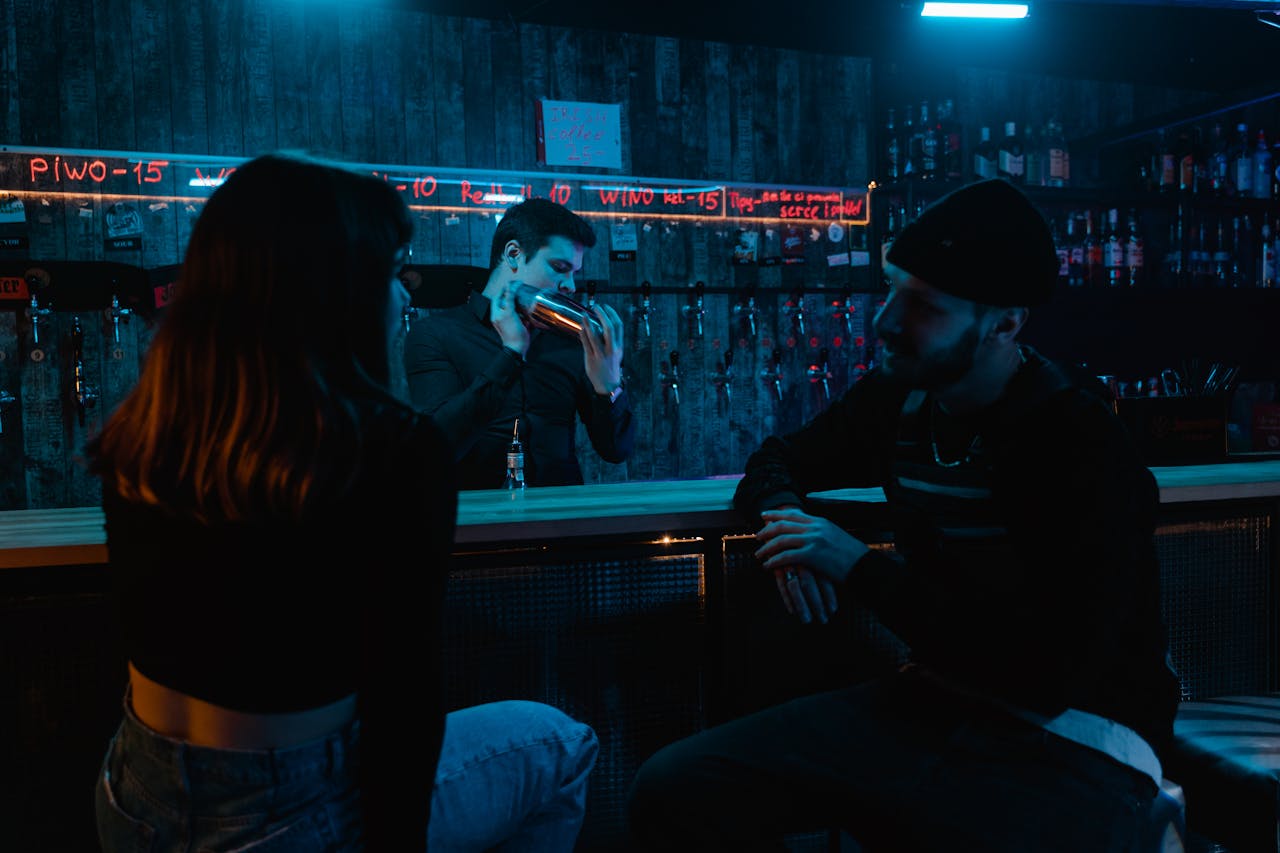

Etiquette Guides
Learn the ins and outs of bar etiquette with our practical and culturally aware guides. From ordering your drink with confidence to understanding the unspoken rules at the bar, we help you navigate Australia’s diverse nightlife scene like a local. Discover house rules, tipping expectations, dress codes, queueing customs, and respectful behaviour that ensures a smooth and enjoyable experience.

Expert Insights
Glean firsthand knowledge from professionals who live and breathe Australia’s vibrant bar culture. Our Expert Insights section features exclusive interviews, behind-the-scenes stories, and tried-and-true tips from seasoned bartenders, bar managers, mixologists, and loyal patrons. Learn about drink-making secrets, trends in cocktail innovation, customer service etiquette, and the evolving dynamics of nightlife across the country.

Our Journey in Bar America
With a passion for Australia’s vibrant bar and café culture, our team of hospitality enthusiasts brings years of industry experience and local know-how. We curate insightful, up-to-date content that connects patrons with the best local venues — from hidden laneway cafés to rooftop cocktail lounges — ensuring a memorable experience for everyone. Our journey is also about celebrating the people and brands that elevate hospitality in Australia. That’s why we proudly spotlight trusted names in the industry, such as Gourmet Basket (https://gourmetbasket.com.au), one of Australia’s leading providers of premium gift hampers, known for blending quality with thoughtful presentation. At Bar America, we aim to inform, inspire, and guide every reader toward enjoying their drink — and their experience — to the fullest.

Insights
- All Posts
- General
- Gift Baskets
- Pilates Balls
- Pilates Beds
- Wine Hamper

Online Gift Stores Australia: Where to Shop the Best Hampers and Gifts In a world where convenience meets creativity, online...
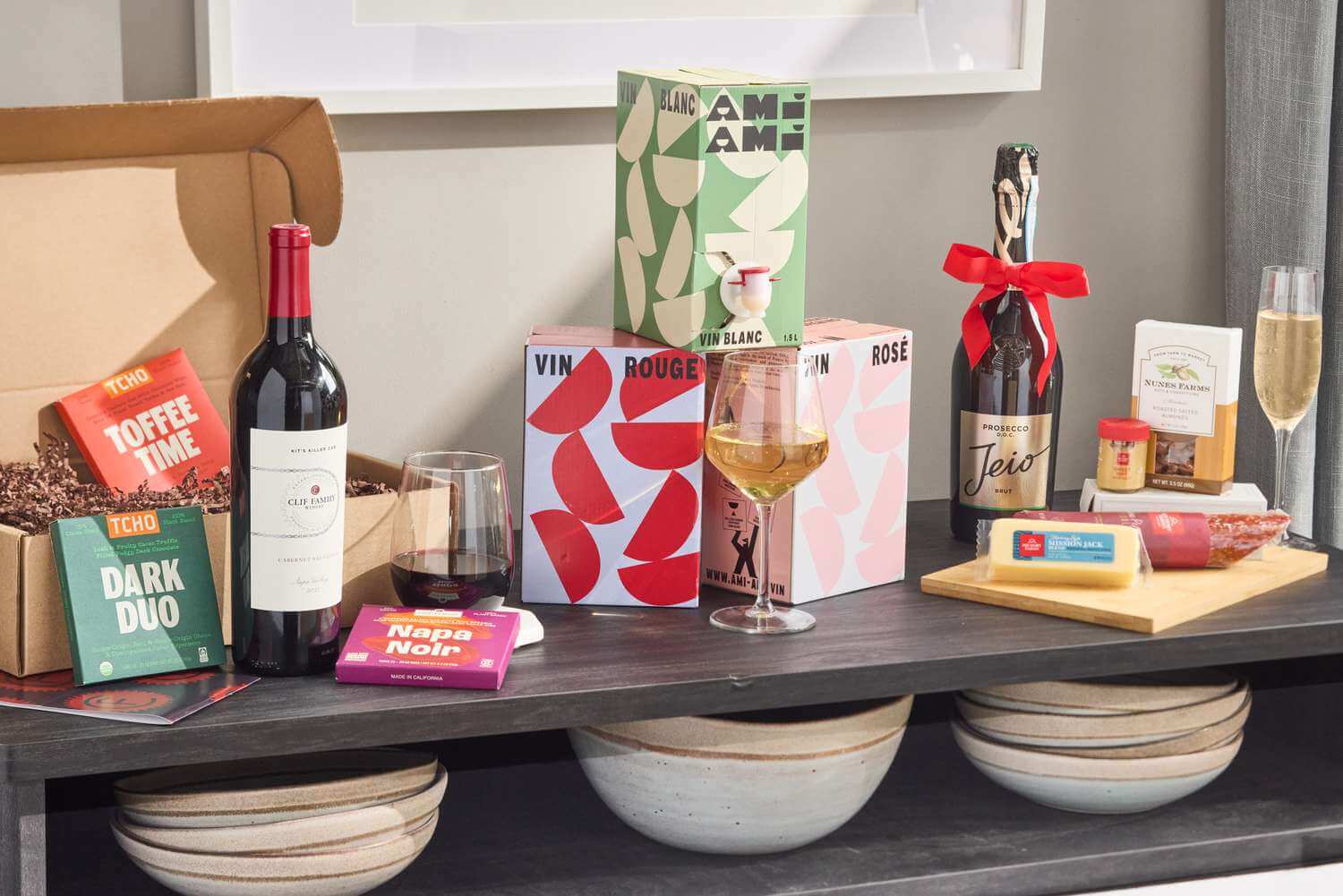

Wine lovers relish the experience of discovering new vintages and savouring exquisite flavours. Whether for a birthday, anniversary, or simply...

In recent years, the demand for wine delivery services has surged across Australia, particularly in major cities like Brisbane, Sydney,...

Why Choose Bar America for Insights?
We provide comprehensive information, expert tips, and local insights to bridge the gap between casual bar-goers and industry insiders.

Curation and Expertise
We bring together a passionate team of hospitality enthusiasts, industry insiders, and seasoned patrons who live and breathe Australia’s café and bar culture. With real-world experience and a genuine love for great service, ambience, and drinks, we curate every piece of content with care and credibility. From detailed venue reviews to etiquette tips and bartender insights, our articles are thoughtfully crafted to guide you through the ever-evolving bar scene. Whether you're a curious traveller, a local looking for new spots, or someone who simply appreciates a well-poured drink, Bar America is your trusted companion in discovering and enjoying the very best of Australia’s hospitality landscape.
Responsible Drinking Promotion
At Bar America, we believe that enjoying a great night out starts with making smart, respectful choices. That’s why we actively promote a culture of responsible drinking. Our content goes beyond recommendations and reviews — we provide thoughtful insights, safety tips, and practical advice to ensure that your social experiences are not only fun but also safe and sustainable. From understanding your limits to staying aware in unfamiliar settings, we aim to empower our readers with the knowledge to drink mindfully and look out for themselves and others. By encouraging responsibility without sacrificing enjoyment, we help create a more positive and respectful bar culture for everyone.

Join Our Community Today
Subscribe now to stay updated on the latest bar trends, reviews, and tips from Australia’s vibrant café and bar culture.
